Disadvantages of Wall Mesh: A Comprehensive Review
The use of wall mesh systems has become increasingly common in recent years. However, users who research suitable wall reinforcement methods are often faced with an important question: what are the disadvantages of wall mesh, and is this system appropriate for their project?
In this article, based on user experience and material standards, we thoroughly examine all weaknesses and limitations of metal mesh systems, including wall mesh structures, welded mesh sheets, wall mesh connectors, and related materials, using a clear yet technical approach to help you make a more accurate decision.
Wall Mesh Disadvantages at a Glance
The table below summarizes the most important disadvantages of wall mesh along with brief technical explanations, providing a quick and practical overview of this system’s weaknesses.
| Disadvantage | Technical Explanation |
|---|---|
| High installation cost | Requires skilled labor and precise tools, increasing overall costs |
| High maintenance cost | Exposure to corrosion increases long-term maintenance expenses |
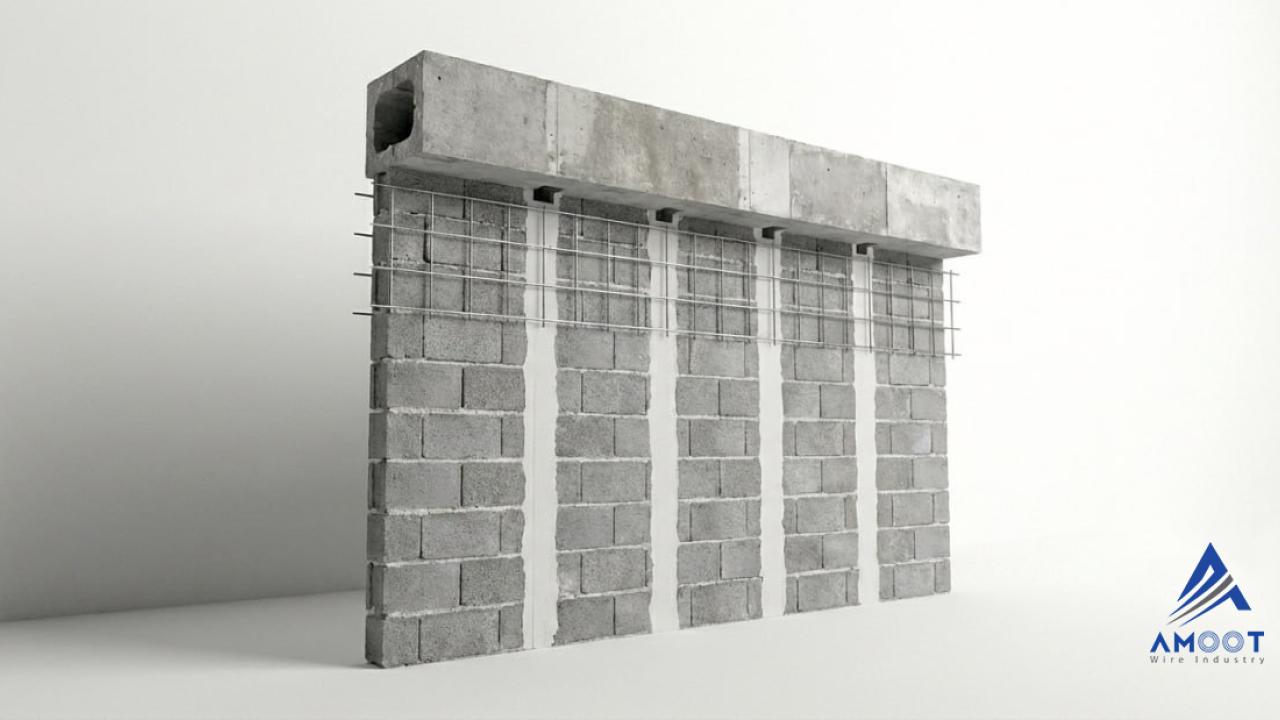
| Heavy structural weight | Steel mesh and welded sheets increase the dead load of the structure |
| Reduced speed in small projects | Preparation and installation are time-consuming and not economical for small-scale work |
| Poor acoustic insulation | Open mesh structure allows sound transmission |
| Insufficient thermal insulation | High thermal conductivity requires additional insulation layers |
| Risk of metal corrosion | Lack of galvanization or inadequate anti-rust coating leads to corrosion |
| Risk of wall settlement | Improper execution or low-quality connections can cause settlement |
| Limited seismic resistance | Performs poorly against lateral loads when used alone |
| Interference with building services | Conflicts with electrical wiring and plumbing installations |
| Complexity in cutting and resizing | Steel mesh rigidity makes dimensional changes difficult |
| Low welding quality | Non-standard welds reduce tensile and bending strength |
Wall Mesh Costs

Cost is always a major concern for employers. In wall mesh systems, the combination of metal mesh, wall mesh connectors, and the need for professional tools makes execution costs higher than alternatives such as rabitz or chicken wire. Additionally, the heavy weight of steel mesh increases transportation costs, which becomes especially noticeable in projects with long transport distances. Many engineers also point out that in small projects, reduced execution speed significantly lowers the economic justification for using wall mesh.
Maintenance and Repair Costs
Beyond initial costs, long-term expenses must also be considered. If the welded mesh is not galvanized or lacks a proper anti-corrosion coating, the risk of rust increases significantly. As a result, wall performance deteriorates over time and repairs become necessary. Experience shows that this issue is more pronounced in humid regions.
Technical Issues and Their Impact on Structural Performance
Mesh spacing, mesh pattern (square or ribbed), and wire diameter are key factors that determine tensile, bending, and shear strength. If any of these parameters fail to meet material standards, the final structure will not achieve the required performance.
Insufficient Acoustic Insulation
Due to the mesh-based wall structure, sound can easily pass through. Many users in residential and office projects report that wall mesh systems fail to provide the expected level of sound insulation.
Insufficient Thermal Insulation
Because of high thermal conductivity, wall mesh systems require additional layers compared to drywall or prefabricated walls, especially in cold or hot climates. Even in standard buildings, improper layering can result in noticeable energy loss.
Increased Dead Load on the Structure
The use of steel mesh and reinforcement networks increases the dead load of the building. This becomes particularly critical in older buildings or structures with load-bearing limitations.
Limited Earthquake Resistance
During earthquakes, lateral forces play a crucial role. Wall mesh alone cannot adequately control these forces and does not provide sufficient resistance unless combined with wall posts or additional structural elements. Structural engineers consider this a serious weakness.
Execution-Related Issues
Wall mesh installation requires high precision. Execution errors such as incorrect mesh spacing or misaligned connectors can lead to wall cracking or settlement. These problems are most commonly observed in projects handled by inexperienced crews.
Interference with Building Installations
Due to the rigidity of steel mesh, electrical conduits and plumbing routes often need modification. This increases execution time and overall cost, a common complaint among employers.
Difficulty in Cutting and Resizing
Mesh sheets and their connectors are not easily cut or resized. Even minor mistakes can cause non-standard deformation, affecting final accuracy and potentially impacting finishing layers such as plaster or putty.
Material Quality Issues
One of the biggest challenges with wall mesh systems is inconsistent market quality. Some products comply with material standards, while others suffer from poor welding quality or inaccurate dimensions. This inconsistency makes final wall performance unpredictable.
Performance Degradation in High Humidity
Especially when the mesh is not galvanized, moisture leads to rust and corrosion of the metal mesh. This negatively affects bending and shear strength. Employer experience in northern regions confirms that this issue is very common.
Comparison of Wall Mesh with Alternative Methods
After thoroughly reviewing the disadvantages of wall mesh, it is reasonable to ask whether better alternatives exist for specific projects. Below is a comparison with common alternatives.
Compared to rabitz, rabitz offers faster installation and easier shaping, making it preferable for lightweight projects.
Compared to drywall systems, drywall is lighter, provides better thermal and acoustic insulation, and does not increase dead load, making it ideal for renovation projects.
Compared to prefabricated walls, prefabricated systems offer higher dimensional accuracy and are well suited for large industrial projects.
Compared to concrete blocks, concrete blocks provide better insulation and require less periodic maintenance.
Compared to wall posts, wall posts perform much better against seismic lateral forces and are often used as a complementary system to wall mesh.
Compared to chicken wire, chicken wire is more flexible and cost-effective for lightweight applications.
Conclusion
This article examined all major disadvantages of wall mesh from technical, executional, and economic perspectives. While wall mesh is a functional system, it has limitations such as high weight, high cost, need for skilled labor, weak insulation performance, and corrosion risk. When executed with standard materials and professional teams, it can perform adequately; however, for small projects or buildings with load limitations, it must be selected with greater caution.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main disadvantages of wall mesh?
High installation cost, increased structural weight, insufficient acoustic and thermal insulation, corrosion risk, and execution-related challenges such as interference with installations.
Is wall mesh suitable for earthquake-prone areas?
Not on its own. It must be combined with wall posts or additional reinforcement to achieve adequate seismic resistance.
Is wall mesh appropriate for small projects?
Generally not recommended due to slower execution and higher costs.
How can corrosion of wall mesh be prevented?
Using galvanized steel mesh, standard anti-corrosion coatings, and proper maintenance is the most effective solution.





